Daily Insights Hub
Your go-to source for the latest trends and insights.
Fair Play or Fair Game? Navigating Smart Contract Fairness
Explore the fine line between fair play and fair game in smart contracts. Discover how to ensure fairness in the digital age!
Understanding Smart Contracts: Are They Truly Fair?
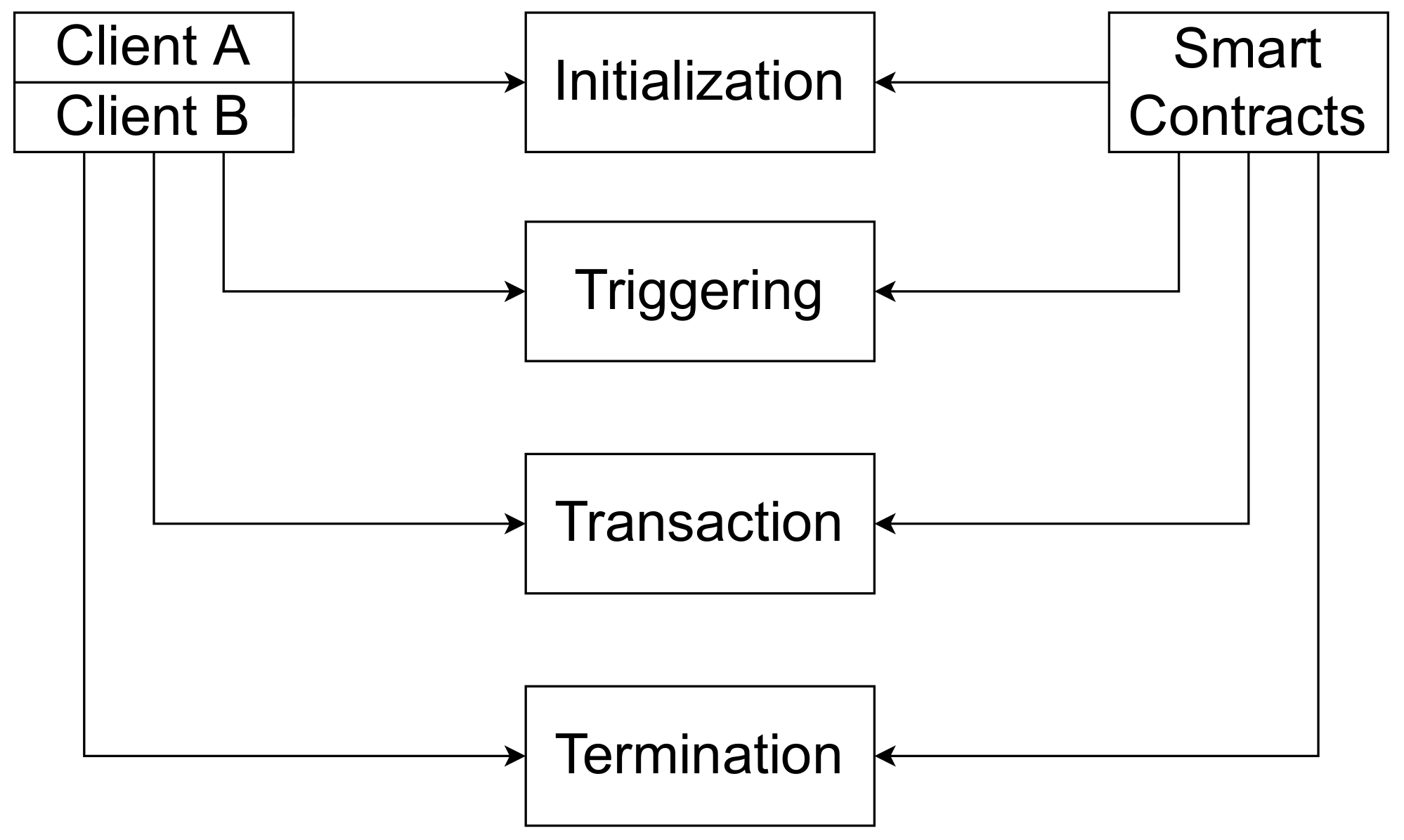
Understanding Smart Contracts is essential in today's digital landscape, particularly as blockchain technology gains traction. These self-executing contracts, with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, promise to enhance transparency and reduce disputes. However, the core question arises: Are they truly fair? While smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, thus reducing the potential for biased decision-making, they also inherit the biases of their creators. A poorly written contract can lead to unintended consequences, raising concerns about fairness and accountability in their execution.
Moreover, the concept of fairness in smart contracts extends beyond their coding; it touches on accessibility and understanding. Many users may lack the technical knowledge to evaluate a smart contract’s terms effectively. This knowledge gap can create a power imbalance where only those with technical expertise can navigate these systems confidently. To foster a genuinely fair environment, it is imperative to prioritize education and transparency in the deployment of smart contracts, ensuring that all parties involved can engage with them on equal footing.
Counter-Strike is a highly competitive first-person shooter game that has gained immense popularity in the gaming community. Players can choose to be part of either the terrorist or counter-terrorist team, each with specific objectives. To enhance your gaming experience, you may want to check out our bc.game promo code for some exclusive benefits!
The Ethics of Smart Contracts: Fair Play vs. Fair Game
The rise of smart contracts has sparked debates about the ethics surrounding their implementation. At the core of this discourse lies the dichotomy between fair play and fair game. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into lines of code, promise to facilitate transactions without the need for intermediaries. However, they also bring forth ethical questions regarding transparency, accountability, and fairness. As users increasingly rely on these automated agreements, the challenge remains: are we ensuring a system that promotes fair play by protecting all parties involved, or are we merely creating a fair game, where those with more technical expertise can exploit the system to their advantage?
Additionally, the idea of fairness in smart contracts extends to their potential impact on society at large. Critics argue that without proper oversight and regulation, these digital agreements could perpetuate existing inequalities and foster environments ripe for abuse. For instance, the intricacies of smart contracts can often disadvantage users who lack the necessary understanding of the underlying technology. Ethical considerations must, therefore, include not just the functionality of smart contracts but also their implications on justice and equity within the digital economy. Embracing a framework that prioritizes fair play over merely a fair game can encourage a more inclusive and ethical approach to the adoption of smart contracts.
How to Identify Fairness in Smart Contract Agreements
In the evolving landscape of blockchain technology, understanding fairness in smart contract agreements is crucial for both developers and users. To identify fairness, one must first assess the transparency of the contract's code. This involves not only reviewing the source code but also ensuring that it is accessible and clear to all parties involved. A smart contract that hides its parameters or contains ambiguous clauses can lead to disputes and unfair outcomes. Additionally, utilizing formal verification methods can help confirm whether the contract executes as intended, thus promoting fairness and trust among users.
Another critical aspect is to evaluate the inclusivity of the smart contract’s design. Fair agreements typically consider the interests of all stakeholders and provide equitable access to contract execution. To determine this, stakeholders should analyze whether the contract includes mechanisms for dispute resolution, survival of party obligations, and the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances. Utilizing community feedback and conducting regular audits can help ensure that smart contracts maintain their integrity and fairness over time, fostering a more reliable blockchain ecosystem.